README
ts-service
ts-service is a TypeScript library for validation and logging.
It depends on joi (validator) and bunyan (logger)
Installation
npm i ts-service
Features
- Input logging (input parameters):
myService: ENTER methodName: {param1: 'foo', param2: 'bar'}
- Output logging (sync and async):
myService: EXIT methodName: {result: 'foobar', anotherProp: 'bar'}
- Error logging with input parameters (see example below).
- Input validation and normalization (example: string type
"2"to number type2).
add(
@schema(Joi.number().required())
a: number,
) {
// `typeof a` will be always 'number'
// even if we pass number string value e.g '2'
// if the input is invalid (null, object, array etc) then an error will be thrown in runtime
}
- Validation with inline annotation.
sendEmail(
@schema(Joi.string().email().required()
email: string
) {
...
}
- Validation with class annotation.
@schema(Joi.object().keys({....}))
class SendEmailValues {
...
}
sendEmail(values: SendEmailValues) {
...
}
Example usage (inline annotation)
file services/CalcService.ts
import * as Joi from 'joi';
import { service, validate, schema } from 'ts-service';
@service
class CalcService {
@validate
add(
@schema(Joi.number().required())
a: number,
@schema(Joi.number().required())
b: number,
) {
return a + b;
}
}
// create your service
export const calcService = new CalcService();
use service
import {calcService} from './services/CalcService';
calcService.add(1, 3); // returns 4
calcService.add('5' as any, '6' as any); // returns 11, input parameters are converted to number types
calcService.add('1' as any, { foo: 'bar' } as any); // logs and throws an error
// NOTE: you shouldn't use casting `as any` in your code. It's used only for a demonstration purpose.
// The service is expected to be called with unknown input (for example: req.body).
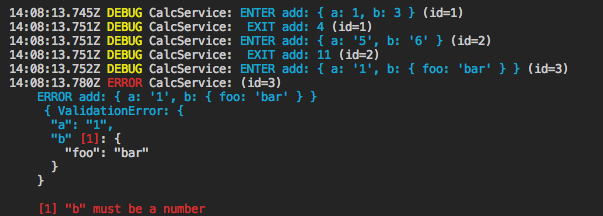
See example under examples/example1.ts. Run it using npm run example1.
Async example usage (class annotation)
file services/UserService.ts
import * as Joi from 'joi';
import { service, validate, schema } from 'ts-service';
@schema(
Joi.object().keys({
name: Joi.string()
.required()
.alphanum(),
email: Joi.string()
.required()
.email(),
password: Joi.string()
.required()
.min(5),
}),
)
class CreateUserValues {
name: string;
email: string;
password: string;
}
@service
class UserService {
@validate
async createUser(values: CreateUserValues) {
const id = 1;
return id;
}
}
// create your service
export const userService = new UserService();
use service
import {userService} from './services/UserService';
await userService.createUser({
name: 'john',
email: 'john@example.com',
password: 'secret',
}); // ok
await userService.createUser({
name: 'john',
email: 'invalid email',
password: 'secret',
}); // throws an error
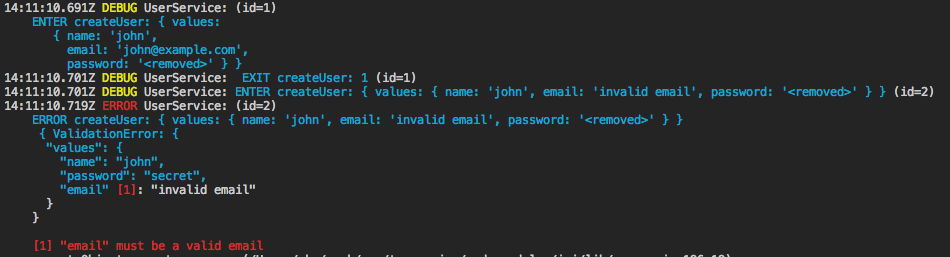
See example under examples/example2.ts. Run it using npm run example2.
Removing security information
By default properties password, token, accessToken are removed from logging.
Additionally you can annotated method with @removeOutput to remove the method result.
Example:
file services/SecurityService.ts
import * as Joi from 'joi';
import { service, validate, schema, removeOutput } from 'ts-service';
@service
class SecurityService {
@validate
@removeOutput
hashPassword(
@schema(Joi.string().required())
password: string,
) {
return 'ba817ef716'; // hash password here
}
}
// create your service
export const securityService = new SecurityService();
use service
import {securityService} from './services/SecurityService';
securityService.hashPassword('secret-password');

See example under examples/example3.ts. Run it using npm run example3.
Configuration
import {configure} from 'ts-service';
configure({
removeFields: string[], // the array of fields not won't be logged to the console, default: ['password', 'token', 'accessToken'],
debug: boolean, // the flag if ENTER and EXIT logging is enabled, (errors are always enabled), default: true
depth: number, // the object depth level when serializing, default: 4
maxArrayLength: number, // the maximum number of elements to include when formatting an array, default: 30
})
You must configure it, before creating any service.
Special properties
if the parameter name is req it's assumed that the object is an express request.
Only properties are logged: method, url, headers, remoteAddress, remotePort.
if the parameter name is res it's assumed that the object is an express response.
Only properties are logged: statusCode, header.
MIT License