README
A React Native component for adding Spokestack to any React Native app.
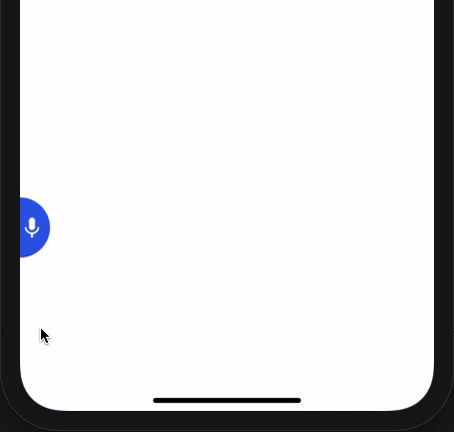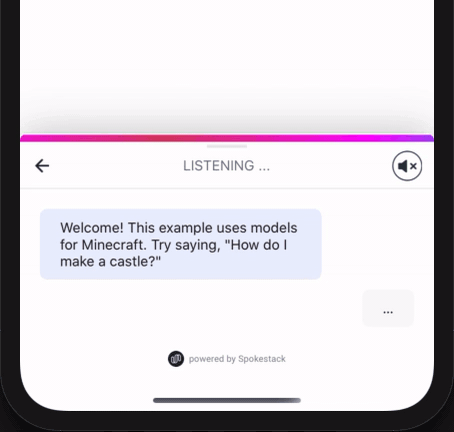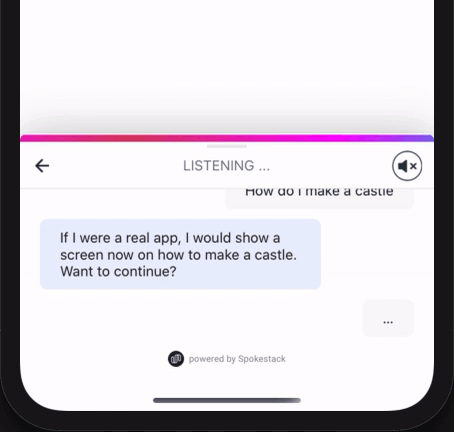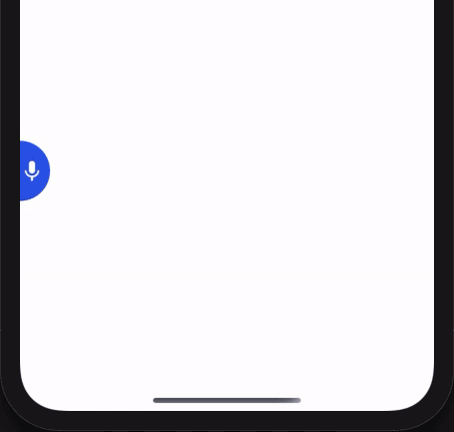
Installation
Install this library with the peer dependencies
A one-liner to install all dependencies
npm install react-native-spokestack-tray react-native-spokestack @react-native-community/async-storage react-native-video react-native-haptic-feedback react-native-linear-gradient react-native-permissions
Each dependency by its usage.
$ npm install react-native-spokestack-tray react-native-spokestack
# Used for storing a simple boolean to turn on/off sound
$ npm install @react-native-community/async-storage
# Used to play TTS audio prompts.
# Despite its name, we think this is one of the best
# plugins (if not the best) for playing audio.
# In iOS, Audio and Video are intertwined anyway.
$ npm install react-native-video
# Used to show an animating gradient when Spokestack listens
$ npm install react-native-linear-gradient
# Used to check microphone and speech recognition permissions
$ npm install react-native-permissions
# Used to generate a haptic whenever Spokestack listens.
# This can be turned off, but the dependency is still needed.
$ npm install react-native-haptic-feedback
Then follow the instructions for each platform to link react-native-spokestack to your project:
iOS installation
iOS details
Set deployment target
react-native-spokestack makes use of relatively new APIs only available in iOS 13+. Make sure to set your deployment target to iOS 13.
First, open XCode and go to Project -> Info to set the iOS Deployment target to 13.0 or higher.
Also, set deployment to 13.0 under Target -> General -> Deployment Info.
Remove invalid library search path
When Flipper was introduced to React Native, some library search paths were set for Swift. There has been a longstanding issue with the default search paths in React Native projects because a search path was added for swift 5.0 which prevented any other React Native libraries from using APIs only available in Swift 5.2 or later. Spokestack-iOS, a dependency of react-native-spokestack makes use of these APIs and XCode will fail to build.
Fortunately, the fix is fairly simple. Go to your target -> Build Settings and search for "Library Search Paths".
Remove "\"$(TOOLCHAIN_DIR)/usr/lib/swift-5.0/$(PLATFORM_NAME)\"" from the list.
Edit Podfile
Before running pod install, make sure to make the following edits.
platform :ios, '13.0'
We also need to use use_frameworks! in our Podfile in order to support dependencies written in Swift.
target 'SpokestackExample' do
use_frameworks!
#...
For the time being, use_frameworks! does not work with Flipper, so we also need to disable Flipper. Remove any Flipper-related lines in your Podfile. In React Native 0.63.2, they look like this:
# X Remove or comment out these lines X
# use_flipper!
# post_install do |installer|
# flipper_post_install(installer)
# end
# XX
react-native-permissions pods
We use react-native-permissions to check and request the Microphone permission (iOS and Android) and the Speech Recognition permission (iOS only). This library separates each permission into its own pod to avoid inflating your app with code you don't use. Add the following pods to your Podfile:
target 'SpokestackTrayExample' do
# ...
permissions_path = '../node_modules/react-native-permissions/ios'
pod 'Permission-Microphone', :path => "#{permissions_path}/Microphone.podspec"
pod 'Permission-SpeechRecognition', :path => "#{permissions_path}/SpeechRecognition.podspec"
Bug in React Native 0.64.0 (should be fixed in 0.64.1)
React Native 0.64.0 broke any projects using use_frameworks! in their Podfiles.
For more info on this bug, see https://github.com/facebook/react-native/issues/31149.
To workaround this issue, add the following to your Podfile:
# Moves 'Generate Specs' build_phase to be first for FBReactNativeSpec
post_install do |installer|
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
if (target.name&.eql?('FBReactNativeSpec'))
target.build_phases.each do |build_phase|
if (build_phase.respond_to?(:name) && build_phase.name.eql?('[CP-User] Generate Specs'))
target.build_phases.move(build_phase, 0)
end
end
end
end
end
pod install
Remove your existing Podfile.lock and Pods folder to ensure no conflicts, then install the pods:
$ npx pod-install
Edit Info.plist
Add the following to your Info.plist to enable permissions. In XCode, also ensure your iOS deployment target is set to 13.0 or higher.
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app uses the microphone to hear voice commands</string>
<key>NSSpeechRecognitionUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app uses speech recognition to process voice commands</string>
Remove Flipper
While Flipper works on fixing their pod for use_frameworks!, we must disable Flipper. We already removed the Flipper dependencies from Pods above, but there remains some code in the AppDelegate.m that imports Flipper. There are two ways to fix this.
- You can disable Flipper imports without removing any code from the AppDelegate. To do this, open your xcworkspace file in XCode. Go to your target, then Build Settings, search for "C Flags", remove
-DFB_SONARKIT_ENABLED=1from flags. - Remove all Flipper-related code from your AppDelegate.m.
In our example app, we've done option 1 and left in the Flipper code in case they get it working in the future and we can add it back.
Edit AppDelegate.m
Add AVFoundation to imports
#import <AVFoundation/AVFoundation.h>
AudioSession category
Set the AudioSession category. There are several configurations that work.
The following is a suggestion that should fit most use cases:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
AVAudioSession *session = [AVAudioSession sharedInstance];
[session setCategory:AVAudioSessionCategoryPlayAndRecord
mode:AVAudioSessionModeDefault
options:AVAudioSessionCategoryOptionDefaultToSpeaker | AVAudioSessionCategoryOptionAllowAirPlay | AVAudioSessionCategoryOptionAllowBluetoothA2DP | AVAudioSessionCategoryOptionAllowBluetooth
error:nil];
[session setActive:YES error:nil];
// ...
Android installation
Android details
ASR Support
The example usage uses the system-provided ASRs (AndroidSpeechRecognizer and AppleSpeechRecognizer). However, AndroidSpeechRecognizer is not available on 100% of devices. If your app supports a device that doesn't have built-in speech recognition, use Spokestack ASR instead by setting the profile to a Spokestack profile using the profile prop.
See our ASR documentation for more information.
Edit root build.gradle (not app/build.gradle)
// ...
ext {
// Minimum SDK is 21
minSdkVersion = 21
// ...
dependencies {
// Minimium gradle is 3.0.1+
// The latest React Native already has this
classpath("com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.5.3")
Edit AndroidManifest.xml
Add the necessary permissions to your AndroidManifest.xml. The first permission is often there already. The second is needed for using the microphone.
<!-- For TTS -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<!-- For wakeword and ASR -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<!-- For ensuring no downloads happen over cellular, unless forced -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
Usage
import SpokestackTray, { listen } from 'react-native-spokestack-tray'
// ...
export default function ConversationHandler({ navigation }) {
return (
<SpokestackTray
clientId={process.env.SPOKESTACK_CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret={process.env.SPOKESTACK_CLIENT_SECRET}
handleIntent={(intent, slots, utterance) => {
switch (intent) {
// These cases would be for all
// the possible intents defined in your NLU.
case 'request.select':
// As an example, search with some service
// with the given value from the NLU
const recipe = SearchService.find(slots.recipe?.value)
// An example of navigating to some scene to show
// data, a recipe in our example.
navigation.navigate('Recipe', { recipe })
return {
node: 'info.recipe',
prompt: 'We found your recipe!'
}
default:
return {
node: 'welcome',
prompt: 'Let us help you find a recipe.'
}
}
}}
// The NLU models are downloaded and then cached
// when the app is first installed.
// See https://spokestack.io/docs/concepts/nlu
// for more info on NLU.
nlu={{
nlu: 'https://somecdn/nlu.tflite',
vocab: 'https://somecdn/vocab.txt',
metadata: 'https://somecdn/metadata.json'
}}
/>
)
}
Including model files in your app bundle
To include model files locally in your app (rather than downloading them from a CDN), you also need to add the necessary extensions so
the files can be included by Babel. To do this, edit your metro.config.js.
const defaults = require('metro-config/src/defaults/defaults')
module.exports = {
resolver: {
// json is already in the list
assetExts: defaults.assetExts.concat(['tflite', 'txt', 'sjson'])
}
}
Then include model files using source objects:
<SpokestackTray
clientId={process.env.SPOKESTACK_CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret={process.env.SPOKESTACK_CLIENT_SECRET}
handleIntent={handleIntent}
wakeword={{
filter: require('./filter.tflite'),
detect: require('./detect.tflite'),
encode: require('./encode.tflite')
}}
nlu={{
model: require('./nlu.tflite'),
vocab: require('./vocab.txt'),
// Be sure not to use "json" here.
// We use a different extension (.sjson) so that the file is not
// immediately parsed as json and instead
// passes a require source object to Spokestack.
// The special extension is only necessary for local files.
metadata: require('./metadata.sjson')
}}
/>
This is not required. Pass remote URLs to the same config options and the files will be downloaded and cached when first calling initialize.
Contributing
See the contributing guide to learn how to contribute to the repository and the development workflow.
Documentation
<SpokestackTray /> Component Props
buttonWidth
• Optional buttonWidth: number (Default: 60)
Width (and height) of the mic button
Defined in
clientId
• clientId: string
Your Spokestack tokens generated in your Spokestack account at https://spokestack.io/account. Create an account for free then generate a token. This is from the "ID" field.
Defined in
clientSecret
• clientSecret: string
Your Spokestack tokens generated in your Spokestack account at https://spokestack.io/account. Create an account for free then generate a token. This is from the "secret" field.
Defined in
closeDelay
• Optional closeDelay: number (Default: 0)
How long to wait to close the tray after speaking (ms)
Defined in
debug
• Optional debug: boolean
Show debug messages from react-native-spokestack
Defined in
duration
• Optional duration: number (Default: 500)
Duration for the tray animation (ms)
Defined in
easing
• Optional easing: EasingFunction (Default: Easing.bezier(0.77, 0.41, 0.2, 0.84))
Easing function for the tray animation
Defined in
exitNodes
• Optional exitNodes: string[]
All nodes in this array should end the conversation and close the tray
Defined in
fontFamily
• Optional fontFamily: string
Font to use for "LISTENING...", "LOADING...", and chat bubble text.
Defined in
gradientColors
• Optional gradientColors: string[] (Default: ["#61fae9", "#2F5BEA"])
Colors for the linear gradient shown when listening Can be any number of colors (recommended: 2-3)
Defined in
greet
• Optional greet: boolean (Default: false)
Whether to greet the user with a welcome message
when the tray opens.
Note: handleIntent must respond to the "greet" intent.
Defined in
haptic
• Optional haptic: boolean (Default: true)
Set this to false to disable the haptic that gets played whenever the tray starts listening.
Defined in
keyword
• Optional keyword: KeywordConfig
Configuration for keyword recognition
The filter, detect, encode, and metadata fields accept 2 types of values.
- A string representing a remote URL from which to download and cache the file (presumably from a CDN).
- A source object retrieved by a
requireorimport(e.g.model: require('./nlu.tflite'))
See https://www.spokestack.io/docs/concepts/keywords to learn more about keyword recognition.
example
// ...
keyword={{
detect: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/UbMeX/detect.tflite',
encode: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/UbMeX/encode.tflite',
filter: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/UbMeX/filter.tflite',
metadata: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/UbMeX/metadata.json'
}}
You can also download models ahead of time and include them from local files. Note: this requires a change to your metro.config.js. For more info, see "Including model files in your app bundle" in the README.md.
// ...
keyword={{
detect: require('./detect.tflite'),
encode: require('./encode.tflite'),
filter: require('./filter.tflite'),
// IMPORTANT: a special extension is used for local metadata JSON files (`.sjson`) when using `require` or `import`
// so the file is not parsed when included but instead imported as a source object. This makes it so the
// file is read and parsed by the underlying native libraries instead.
metadata: require('./metadata.sjson')
}}
Keyword configuration also accepts a classes field for when metadata is not specified.
// ...
keyword={{
detect: require('./detect.tflite'),
encode: require('./encode.tflite'),
filter: require('./filter.tflite'),
classes: ['one', 'two', 'three]
}}
Defined in
minHeight
• Optional minHeight: number (Default: 170)
Minimum height for the tray
Defined in
nlu
• nlu: NLUConfig
The NLU Tensorflow Lite model (.tflite), JSON metadata, and NLU vocabulary (.txt)
All 3 fields accept 2 types of values.
- A string representing a remote URL from which to download and cache the file (presumably from a CDN).
- A source object retrieved by a
requireorimport(e.g.model: require('./nlu.tflite'))
See https://spokestack.io/docs/concepts/nlu to learn more about NLU.
// ...
nlu={{
model: 'https://somecdn.com/nlu.tflite',
vocab: 'https://somecdn.com/vocab.txt',
metadata: 'https://somecdn.com/metadata.json'
}}
You can also pass local files. Note: this requires a change to your metro.config.js. For more info, see "Including model files in your app bundle" in the README.md.
// ...
nlu={{
model: require('./nlu.tflite'),
vocab: require('./vocab.txt'),
// IMPORTANT: a special extension is used for local metadata JSON files (`.sjson`) when using `require` or `import`
// so the file is not parsed when included but instead imported as a source object. This makes it so the
// file is read and parsed by the underlying native libraries instead.
metadata: require('./metadata.sjson')
}}
Defined in
orientation
• Optional orientation: "left" | "right" (Default: "left")
The tray button can be oriented on either side of the screen
Defined in
primaryColor
• Optional primaryColor: string (Default: "#2f5bea")
This color is used to theme the tray and is used in the mic button and speech bubbles.
Defined in
profile
• Optional profile: PipelineProfile
The Spokestack config profile to pass to react-native-spokestack. These are available from react-native-spokestack starting in version 4.0.0.
If Wakeword config files are specified, the default will be
TFLITE_WAKEWORD_NATIVE_ASR.
Otherwise, the default is PTT_NATIVE_ASR.
import SpokestackTray from 'react-native-spokestack-tray'
import { PipelineProfile } from 'react-native-spokestack'
// ...
<SpokestackTray
profile={PipelineProfile.TFLITE_WAKEWORD_SPOKESTACK_ASR}
// ...
Defined in
refreshModels
• Optional refreshModels: boolean
Use this sparingly to refresh the
wakeword, keyword, and NLU models on device
(force overwrite).
<SpokestackTray refreshModels={process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'} ... />
Defined in
sayGreeting
• Optional sayGreeting: boolean (Default: true)
Whether to speak the greeting or only display a chat bubble with the greet message, even if sound is on.
Defined in
soundOffImage
• Optional soundOffImage: ReactNode (Default: (
<Image source={soundOffImage} style={{ width: 30, height: 30 }} />
))
Replace the sound off image by passing a React Image component
Defined in
soundOnImage
• Optional soundOnImage: ReactNode (Default: (
<Image source={soundOnImage} style={{ width: 30, height: 30 }} />
))
Replace the sound on image by passing a React Image component
Defined in
spokestackConfig
• Optional spokestackConfig: Partial<SpokestackConfig>
Pass options directly to the Spokestack.initialize() function from react-native-spokestack. See https://github.com/spokestack/react-native-spokestack for available options.
Defined in
startHeight
• Optional startHeight: number (Default: 220)
Starting height for tray
Defined in
style
• Optional style: false | RegisteredStyle<ViewStyle> | Value | AnimatedInterpolation | WithAnimatedObject<ViewStyle> | WithAnimatedArray<false | ViewStyle | RegisteredStyle<ViewStyle> | RecursiveArray<false | ViewStyle | RegisteredStyle<ViewStyle>> | readonly (false | ViewStyle | RegisteredStyle<ViewStyle>)[]>
This style prop is passed to the tray's container
Defined in
ttsFormat
• Optional ttsFormat: TTSFormat (Default: TTSFormat.TEXT)
The format for the text passed to Spokestack.synthesize
Defined in
voice
• Optional voice: string (Default: "demo-male")
A key for a voice in Spokestack TTS, passed to Spokestack.synthesize. This may only be changed if you have created a custom voice using a Spokestack Maker account. See https://spokestack.io/pricing#maker. If not specified, Spokestack's Free "demo-male" voice is used.
Defined in
wakeword
• Optional wakeword: WakewordConfig
The NLU Tensorflow Lite models (.tflite) for wakeword.
All 3 fields accept 2 types of values.
- A string representing a remote URL from which to download and cache the file (presumably from a CDN).
- A source object retrieved by a
requireorimport(e.g.model: require('./nlu.tflite'))
See https://spokestack.io/docs/concepts/wakeword-models to learn more about Wakeword
Spokestack offers sample wakeword model files ("Spokestack"):
// ...
wakeword={{
detect: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/hgmYb/detect.tflite',
encode: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/hgmYb/encode.tflite',
filter: 'https://s.spokestack.io/u/hgmYb/filter.tflite'
}}
You can also download these models ahead of time and include them from local files. Note: this requires a change to your metro.config.js. For more info, see "Including model files in your app bundle" in the README.md.
// ...
wakeword={{
detect: require('./detect.tflite'),
encode: require('./encode.tflite'),
filter: require('./filter.tflite')
}}
Defined in
Methods
editTranscript
▸ Optional editTranscript(transcript): string
Edit the transcript before classification and before the user response bubble is shown.
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
transcript |
string |
Returns
string
Defined in
handleIntent
▸ handleIntent(intent, slots?, utterance?): [IntentResult](#IntentResult)
This function takes an intent from the NLU and returns an object with a unique conversation node name (that you define) and a prompt to be processed by TTS and spoken.
Note: the prompt is only shown in a chat bubble if sound has been turned off.
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
intent |
string |
slots? |
SpokestackNLUSlots |
utterance? |
string |
Returns
[IntentResult](#IntentResult)
Defined in
onClose
▸ Optional onClose(): void
Called whenever the tray has closed
Returns
void
Defined in
onError
▸ Optional onError(e): void
Called whenever there's an error from Spokestack
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
e |
SpokestackErrorEvent |
Returns
void
Defined in
onOpen
▸ Optional onOpen(): void
Called whenever the tray has opened
Returns
void
Defined in
IntentResult
data
• Optional data: any
Any other data you might want to add
Defined in
noInterrupt
• Optional noInterrupt: boolean
Set to true to stop the wakeword recognizer
during playback of the prompt.
Defined in
node
• node: string
A user-defined key to indicate where the user is in the conversation
Include this in the exitNodes prop if Spokestack should not listen
again after saying the prompt.
Defined in
prompt
• prompt: string
Will be processed into Speech unless the tray is in silent mode
Defined in
<SpokestackTray /> Component Methods
These methods are available from the SpokestackTray component. Use a React ref to access these methods.
const spokestackTray = useRef(null)
// ...
<SpokestackTray ref={spokestackTray}
// ...
spokestackTray.current.say('Here is something for Spokestack to say')
Note: In most cases, you should call listen instead of open.
open
▸ open(): void
Open the tray, greet (if applicable), and listen
Returns
void
Defined in
close
▸ close(): void
Close the tray, stop listening, and restart wakeword
Returns
void
Defined in
say
▸ say(input): Promise<void>
Passes the input to Spokestack.synthesize(), plays the audio, and adds a speech bubble.
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
input |
string |
Returns
Promise<void>
Defined in
addBubble
▸ addBubble(bubble): void
Add a bubble (system or user) to the chat interface
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
bubble |
Bubble |
Returns
void
Defined in
Bubble
isLeft
• isLeft: boolean
Defined in
src/components/SpeechBubbles.tsx:9
text
• text: string
Defined in
src/components/SpeechBubbles.tsx:8
toggleSilent
▸ toggleSilent(): Promise<boolean>
Toggle silent mode
Returns
Promise<boolean>
Defined in
isSilent
▸ isSilent(): boolean
Returns whether the tray is in silent mode
Returns
boolean
Defined in
Spokestack Functions
These functions are available as exports from react-native-spokestack-tray
listen
▸ listen(): Promise<void>
Tells the Spokestack speech pipeline to start listening. Also requests permission to listen if necessary. It will attempt to start the pipeline before activating if not already started. This function will do nothing if the app is in the background.
import { listen } from 'react-native-spokestack-tray'
try {
await listen()
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
Returns
Promise<void>
Defined in
stopListening
▸ stopListening(): Promise<void>
Returns
Promise<void>
Defined in
isListening
▸ Const isListening(): Promise<boolean>
Returns whether Spokestack is currently listening
console.log(`isListening: ${await isListening()}`)
Returns
Promise<boolean>
Defined in
isInitialized
▸ Const isInitialized(): Promise<boolean>
Returns whether Spokestack has been initialized
console.log(`isInitialized: ${await isInitialized()}`)
Returns
Promise<boolean>
Defined in
isStarted
▸ Const isStarted(): Promise<boolean>
Returns whether the speech pipeline has been started
console.log(`isStarted: ${await isStarted()}`)
Returns
Promise<boolean>
Defined in
addEventListener
▸ Const addEventListener(eventType, listener, context?): EmitterSubscription
Bind to any event emitted by the native libraries The events are: "recognize", "partial_recognize", "error", "activate", "deactivate", and "timeout". See the bottom of the README.md for descriptions of the events.
useEffect(() => {
const listener = addEventListener('recognize', onRecognize)
// Unsubscribe by calling remove when components are unmounted
return () => {
listener.remove()
}
}, [])
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
eventType |
string |
listener |
(event: any) => void |
context? |
Object |
Returns
EmitterSubscription
Defined in
removeEventListener
▸ Const removeEventListener(eventType, listener): void
Remove an event listener
removeEventListener('recognize', onRecognize)
Parameters
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
eventType |
string |
listener |
(...args: any[]) => any |
Returns
void
Defined in
removeAllListeners
▸ Const removeAllListeners(): void
Remove any existing listeners
componentWillUnmount() {
removeAllListeners()
}
Returns
void
Defined in
Events
Use addEventListener(), removeEventListener(), and removeAllListeners() to add and remove events handlers. All events are available in both iOS and Android.
| Name | Data | Description |
|---|---|---|
| recognize | { transcript: string } |
Fired whenever speech recognition completes successfully. |
| partial_recognize | { transcript: string } |
Fired whenever the transcript changes during speech recognition. |
| start | null |
Fired when the speech pipeline starts (which begins listening for wakeword or starts VAD). |
| stop | null |
Fired when the speech pipeline stops. |
| activate | null |
Fired when the speech pipeline activates, either through the VAD, wakeword, or when calling .activate(). |
| deactivate | null |
Fired when the speech pipeline deactivates. |
| play | { playing: boolean } |
Fired when TTS playback starts and stops. See the speak() function. |
| timeout | null |
Fired when an active pipeline times out due to lack of recognition. |
| trace | { message: string } |
Fired for trace messages. Verbosity is determined by the traceLevel option. |
| error | { error: string } |
Fired when there's an error in Spokestack. |
When an error event is triggered, any existing promises are rejected.
Checking speech permissions
These utility functions are used by Spokestack to check microphone permission on iOS and Android and speech recognition permission on iOS.
checkSpeech
▸ checkSpeech(): Promise<boolean>
This function can be used to check whether the user has given the necessary permission for speech. On iOS, this includes both microphone and speech recnogition. On Android, only the microphone is needed.
import { checkSpeech } from 'react-native-spokestack-tray'
// ...
const hasPermission = await checkSpeech()
Returns
Promise<boolean>
Defined in
requestSpeech
▸ requestSpeech(): Promise<boolean>
This function can be used to actually request the necessary permission for speech. On iOS, this includes both microphone and speech recnogition. On Android, only the microphone is needed.
Note: if the user has declined in the past on iOS, the user must be sent to Settings.
import { requestSpeech } from 'react-native-spokestack-tray'
// ...
const hasPermission = await requestSpeech()
Returns
Promise<boolean>
Defined in
License
MIT
