README
node-red-contrib-ui-alarm-clock
A node-red-ui alarm clock for the Node-RED Dashboard.
Based on the awesome node-red-contrib-ui-time-scheduler
Install
You can install this node directly from the "Manage Palette" menu in the Node-RED interface.
Alternatively, run the following command in your Node-RED user directory - typically ~/.node-red on Linux or %HOMEPATH%\.nodered on Windows
npm install node-red-contrib-ui-alarm-clock
Requirements
node-red v0.19 or above
node-red-dashboard v2.10.0 (v2.15.4 or above would be ideal)
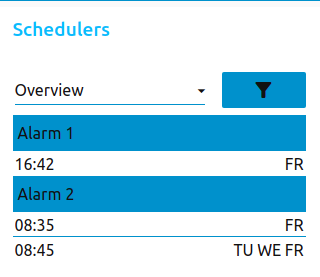
Usage
Add a alarm-clock-node to your flow. Open the dashboard, you will see an empty list. Click the plus sign at the top right corner of the node to create a new timer.
Input
You can inject timers via a msg property payload (see restoring schedules after a reboot section). If the injected msg has a property disableAlarm or enableAlarm the node will disable/enable the alarms output. Disabling/enabling works both with alarm name and index.
If you inject getStatus you can get the next trigger for each alarm (epoch).
Output
Whenever you add, edit or delete a timer a JSON string is sent to the nodes top output. This JSON string contains all timers and settings.
Every other output (number of total outputs depends on how many alarms you have added) emits true once an alarm is triggered. Adjusting the refresh rate is possible within the node's options.
Restoring schedules after a reboot
You can use the JSON string from the nodes top output to directly inject timers after a (re)boot or (re)deploy. See examples dir.
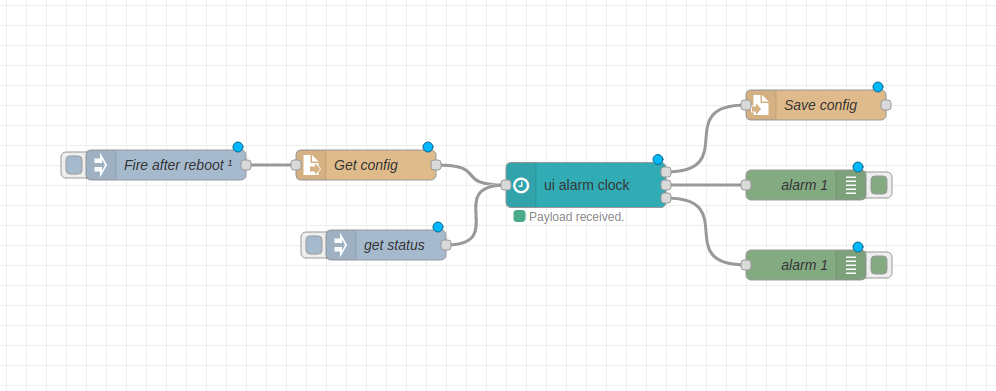
If you changed the node-red contextStorage to localfilesystem, timers are automatically saved and restored after a reboot.
History
Find the changelog here.